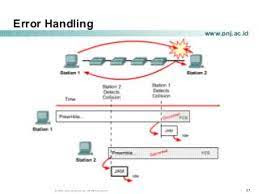
Bandung, Telkom University - To pass the CCNA, Intro, and ICND exams, you need to know the details and pay attention. (Being a master network administrator or engineer is also about paying attention to details, so this makes perfect sense!) Such details know the difference between error detection and troubleshooting . These terms are sometimes used interchangeably, but they are not the same.
Error detection is just that - just error detection. There are two common error detection methods in the data link layer of the OSI model: FCS (Frame Check Sequence) and CRC (Cyclical Redundancy Check). A formula is run on the data in the frame and the result is sent along with the data. The receiver runs the equations again, but this time if the results are the same, the frame is considered valid. If the results are different, the frame is considered corrupted and discarded.
Note that FCS and CRC do nothing with retransmissions. They are strictly error detection schemes. As a troubleshooting example, let's look at the transport layer where TCP runs. TCP performs reliable delivery. The reason we call this "reliable" is that TCP uses sequence numbers to detect missing segments. If the sender determines from the sequence number that the remote host did not receive any of the transmitted segments, the sender retransmits the missing segments.
The key to keeping the terms straight in your head is to remember that while both error detection and error recovery both detect problems, only error recovery does anything about it. It's also worth reading an exam question twice when you see either term!